1. Transformers
Definition: A transformer is a device that utilizes the principle of electromagnetic induction to alter alternating voltage. Its primary components are the primary winding, secondary winding, and iron core (magnetic core).
Working Principle: The transformer operates based on the law of electromagnetic induction. When an alternating voltage is applied to the primary coil, it generates an alternating magnetic flux within the iron core. This flux passes through the secondary coil, inducing an electromotive force (EMF) within it. Due to the difference in the number of turns between the primary and secondary coils, the magnitude of the induced EMF varies, thereby achieving voltage transformation.
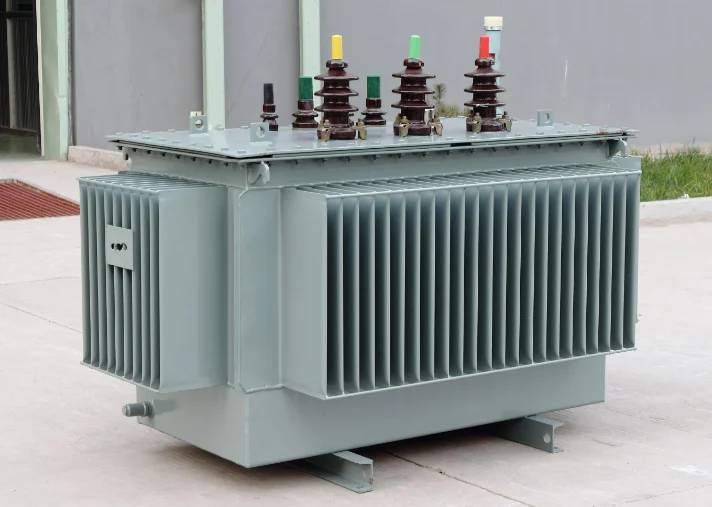

Characteristics: Transformers perform multiple functions, including voltage conversion, current transformation, impedance matching, isolation, and voltage stabilization. As fundamental equipment in power transmission and distribution, they are widely used in industrial, agricultural, transportation, and urban community applications.
2. Rectifier
Definition: A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current (AC), which reverses direction intermittently, into direct current (DC), where current flows in only one direction.
Working Principle: The rectifier operates based on the unidirectional conductivity of semiconductors. During rectification, the unidirectional conductivity of diodes is utilized to filter out either the negative half-cycle or positive half-cycle of the AC, retaining only the positive or negative half-cycle current to produce DC.
Characteristics: Rectifiers feature a simple structure, reliable operation, and high efficiency. They are widely used in electronic circuits, power supply equipment, communication systems, and other fields.
3. Inverter
Definition: An inverter is a converter that transforms DC power (from batteries or storage batteries) into AC power with fixed frequency and voltage or variable frequency and voltage.
Working Principle: The inverter's operation relies on the on-off control of semiconductor switches. When DC power is input to the inverter, it converts DC to AC by controlling the switching of these semiconductor switches. During this process, the inverter's control logic adjusts the switching duration as needed to achieve the desired AC frequency and voltage.
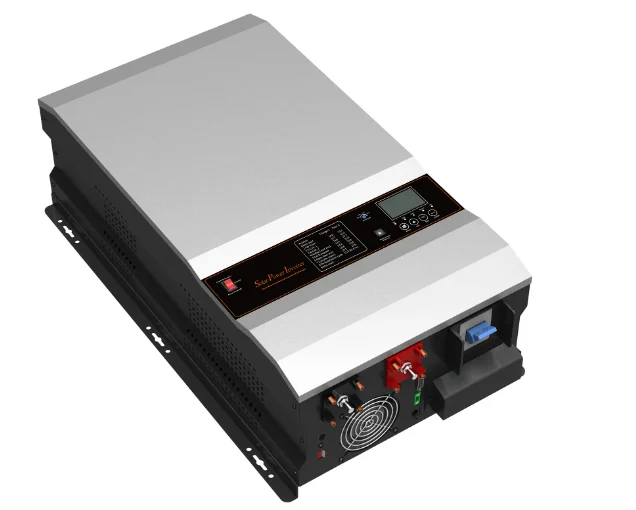

Characteristics: Inverters are characterized by high efficiency, stability, and reliability. Their ability to convert DC to AC makes them widely applicable in scenarios requiring AC power, such as solar power generation systems and electric vehicle charging systems.
4. Differences Between Transformers, Rectifiers, and Inverters
Functional Differences: Transformers primarily alter AC voltage, enabling conversion of voltage, current, and impedance; Rectifiers primarily convert AC to DC; Inverters primarily convert DC to AC.
Structural Differences: Transformers mainly consist of primary coils, secondary coils, and iron cores; Rectifiers primarily comprise semiconductor components like diodes; Inverters include inverter bridges, control logic, and filter circuits.
Application Differences: Transformers are widely used in power transmission and distribution systems, industrial equipment, and household appliances; rectifiers find extensive application in power supply equipment, communication systems, and electronic devices; inverters are primarily employed in solar power generation systems, electric vehicle charging systems, and UPS power supplies.
5. Practical Application Examples
Transformers: Within power grids, transformers convert high-voltage electricity to low-voltage levels for use in residential and commercial areas. Additionally, they facilitate power transmission and distribution within electrical systems.
Rectifiers: In communication systems, rectifiers convert AC power to DC power for supplying communication equipment. Within electronic devices, rectifiers are frequently integrated as components of power supply modules, converting AC to DC for equipment operation.
Inverters: In solar power generation systems, inverters convert the DC electricity generated by solar panels into AC electricity for grid connection and supply to homes or businesses. In electric vehicle charging systems, inverters transform AC electricity from the grid into DC electricity for charging electric vehicles.
As a professional manufacturer and wholesaler of charging adapters, Macable offers a wide range of low-voltage transformers that comply with international certification standards to meet the needs of global consumers. We are committed to providing efficient, safe, and environmentally-friendly charging solutions, offering users a smarter and more convenient charging experience.
